Tasks
SeeDev consists of two subtasks. Participants can choose to participate in either (or both) of these tasks.
Binary relation extraction task (SeeDev-binary)
Systems are evaluated for their ability to extract relations involving two entity arguments. Entity annotations are provided.
Full event extraction task (SeeDev-full)
Systems are evaluated for their ability to extract all types of events, including events involving more than two entities. There is no trigger word in the SeeDev event representation. Entity annotations are provided.
Entities and events are specified in the information representation scheme described below.
Results will be evaluated using precision, recall and F-measure. We plan to focus on Interaction and Regulation relations because the knowledge they carry is more valuable to plant scientists.
Information representation scheme
The SeeDev representation scheme defines 16 entity types, which can be grouped into higher-level classes:
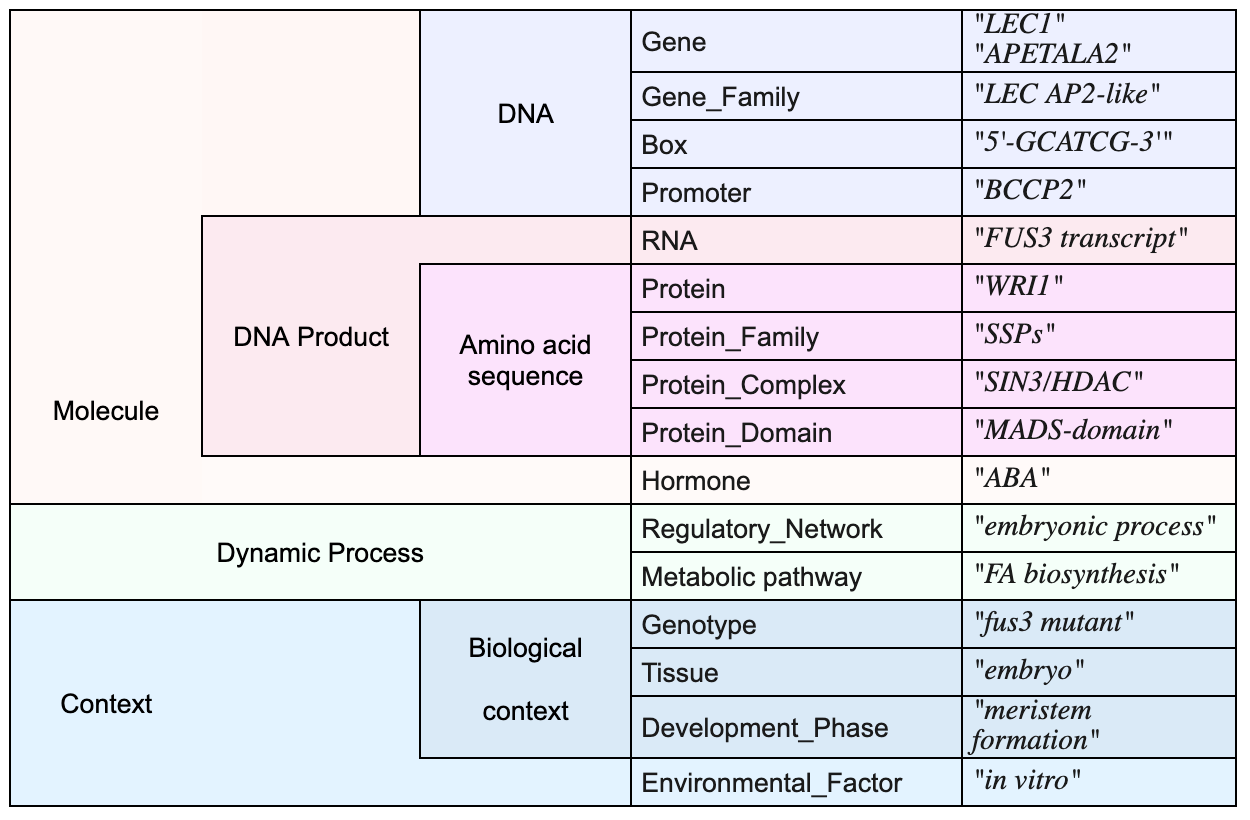
These entities participates in 21 types of events that can be grouped into five categories:
Where and When • Presence_In_Genotype • Occurrence_In_Genotype • Presence_At_Stage • Occurrence_During • Localization
Function • Involvement_In_Process •Transcription_Or_Translation • Functional_Equivalence | Regulation • Regulation_Of_Accumulation • Regulation_Of_Development_Phase • Regulation_Of_Expression • Regulation_Of_Molecule_Activity • Regulation_Of_Process • Regulation_Of_Tissue_Development
| Composition and Membership • Primary_Structure_Composition • Protein_Complex_Composition • Protein_Domain_Composition • Family_Membership • Sequence_Identity
Interaction • Interaction • Binding |
Each event type can be associated with the Negation modality. Events can have between two and eight arguments.
The binary event extraction subtask uses a simplified version of the representation scheme including only binary relations. In this version, n-ary events are decomposed into binary relations according to specific rules. Event labels are the same as for the complete version, except for the Is_Linked_To relation, which is specific to the binary framework.
The detailed formal representation including the role names of the event arguments can be found here.
Event arguments are strongly typed, which means that all types of entities are not possible as event arguments. The possible combinations of entity types per event, i.e. event signatures, are specified here.